|
 |
Graduate Course on machine learning, pattern recognition, neural nets,
statistical modeling.
Instructor: Yann LeCun, 715 Broadway, Room 1220, 212-998-3283, yann [ a t ] cs.nyu.edu
Teaching Assistant: Y-Lan Boureau, 715 Broadway, Room 1206, 212-998-3474, ylan [ a t ] cs.nyu.edu
Classes: Tuesdays 5:00-6:50PM, Room 1221, 715 Broadway.
Office Hours for Prof. LeCun: Wednesdays 5:00-7:00 PM.
Please send an email to Prof. LeCun prior to an office hour visit.
office hours for TA: Tuesdays 3:00-5:00 PM
Click here for schedule and course material >>>
Click here for the list of assignments and final projects >>>
|
|
This course will be an updated version of G22.2565.001
taught in the Fall of 2007.
This course will cover a wide variety of topics in machine learning,
pattern recognition, statistical modeling, and neural computation.
The course will cover the mathematical methods and theoretical
aspects, but will primarily focus on algorithmic and practical issues.
Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition methods are at the core of
many recent advances in "intelligent computing". Current applications
include machine perception (vision, audition, speech recognition),
control (process control, robotics), data mining, time-series
prediction (e.g. in finance), natural language processing, text mining
and text classification, bio-informatics, neural modeling,
computational models of biological processes, and many other areas.
|
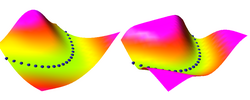
Energy-Based Models
|
| Who Can Take This Course? |
|
This course can be useful to all students who would want to use or
develop statistical modeling methods. This includes students in CS
(AI, Vision, Graphics), Math (System Modeling), Neuroscience (Computational
Neuroscience, Brain Imaging), Finance (Financial modeling and
prediction), Psychology (Vision), Linguistics, Biology (Computational
Biology, Genomics, Bio-informatics), and Medicine (Bio-Statistics,
Epidemiology).
The only formal pre-requisites are familiarity with computer
programming and linear algebra, but the course relies heavily on such
mathematical tools as probability and statistics, multi-variate
calculus, and function optimization. The basic mathematical
concepts will be introduced when needed, but students will be
expected to assimilate a non-trivial amount of mathematical
concepts in a fairly short time.
Although this is a graduate-level course, highly motivated
undergraduates at the senior level with a good math background can
take this class. A few juniors have even taken this class
successfully in the past.
|

|
The topics studied in the course include:
- the basics of inductive inference, learning, and generalization.
- linear classifiers: perceptron, LMS, logistic regression.
- non-linear classifiers with linear parameterizations:
basis-function methods, boosting, support vector machines.
- multilayer neural networks, backpropagation
- heterogeneous learning systems
- graph-based models for sequences: hidden Markov models,
finite-state transducers, recurrent networks.
- unsupervised learning: density estimation,
clustering, and dimensionality reduction methods.
- introduction to graphical models and factor graphs
- approximate inference, sampling.
- optimization methods in learning: gradient-based methods,
second-order methods, Expectation-Maximization.
- objective functions: maximum likelihood, maximum a-posteriori,
discriminative criteria, maximum margin.
- the bias-variance dilemma, regularization, model selection.
- applications in vision, speech, language, forecasting,
and biological modeling.
By the end of the course, students will be able to not only understand
and use the major machine learning methods, but also implement, apply
and analyze them.
|
|
The best way (some would say the only way) to understand an algorithm
is to implement it and apply it. Building working systems is also a
lot more fun, more creative, and more relevant than taking formal exams.
Therefore students will be evaluated primarily (almost exclusively) on
programming projects given on a 2 week cycle, and on a final project.

Automatic
Face Detection
|
Linear algebra, vector calculus, elementary statistics and probability
theory. Good programming ability is a must: most assignements will
consist in implementing algorithms studied in class.
The course will include a short tutorial on the
Lush language, a simple
interpreted language for numerical applications.
Lush can be downloaded and installed on Linux,
Mac OS-X, and Windows (under Cygwin).
See Chris Poultney's
notes on installing Lush under Cygwin.
Lush is available on the CIMS
workstations and servers (Sun and Linux) available for student use.
Programming projects may be implemented in any language, (C, C++,
Java, Matlab, Lisp, Python,...) but the use of a high-level
interpreted language with good numerical support and good support
for vector/matrix algebra is highly recommended (Lush, Matlab,
Octave...). Some assignments require the use of an object-oriented
language.
Also, for most assignments, a code skeleton in Lush will be
provided.
|

Invariant Object Recognition
|
Register to the course's mailing list.
|
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning, by Christopher
Bishop. Springer, August 2006.
NOTES: 13) The publisher just released the first edition of this book on
August 28, 2006, so you might have to wait a few days before getting
it. (2) this is a different book from past years; (3) This is not
Bishop's previous book called Neural Networks and Pattern Recognition;
The textbook can be used for reference, but I will not follow it very
closely.
The following books can also be used for complementary material
(you can get copies from the library):
Other Books of Interest
- C. Bishop: "Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition", Oxford
University Press, 1996. Pretty much superseded by Bishop's lates book.
- S. Haykin: "Neural Networks, a comprehensive foundation",
Prentice Hall, 1999 (second edition).
- Tom Mitchell: "Machine Learning", McGraw Hill, 1997.
|

automatic obstacle avoidance |
| Machine Learning Research at NYU |
Please have a look at the research project page of the
Computational and Biological Learning Lab for a few example
of machine learning research at NYU.
There are numerous opportunities for independent studies and even
undergraduate research projects. Contact Prof. LeCun for details.
Code
- Lush: A simple language for quick
implementation of, and experimentation with, numerical algorithms
(for Linux, Mac, and Windows/Cygwin). Many algorithms described in this
course are implemented in the Lush library. Lush is available on the
department's Sun machines that are freely accessible to NYU graduate
students. See Chris Poultney's
notes on installing Lush under Cygwin.
- Torch: A C++ library for machine learning.
Lush is installed on the department's PCs. It will soon be available
on the Sun network as well.
Papers
Some of those papers are available in the DjVu format.
The viewer/plugins for Windows, Linux, Mac, and various Unix flavors are
available here.
Y. LeCun, S. Chopra, R. Hadsell, F.-J. Huang, M.-A. Ranzato,
"A Tutorial on Energy-Based Learning",
in Predicting Structured Outputs, MIT Press 2006.
[PDF]
[DjVu]
- Y. LeCun, L. Bottou, Y. Bengio, and P. Haffner,
"Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition,"
Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 86, no. 11, pp. 2278-2324, Nov. 1998.
[PS.GZ]
[DjVu]
- Y. LeCun, L. Bottou, G. Orr, and K. Muller, "Efficient BackProp,"
in Neural Networks: Tricks of the trade, (G. Orr and Muller K., eds.), 1998.
[PS.GZ]
[DjVu]
- P. Simard, Y. LeCun, J. Denker, and B. Victorri,
"Transformation Invariance in Pattern Recognition, Tangent Distance and Tangent Propagation,"
in Neural Networks: Tricks of the trade, (G. Orr and Muller K., eds.), 1998.
[PS.GZ]
[DjVu]
Publications, Journals
Conference Sites
Datasets
|
 |