Colossus Computer
Bletchley Park, England
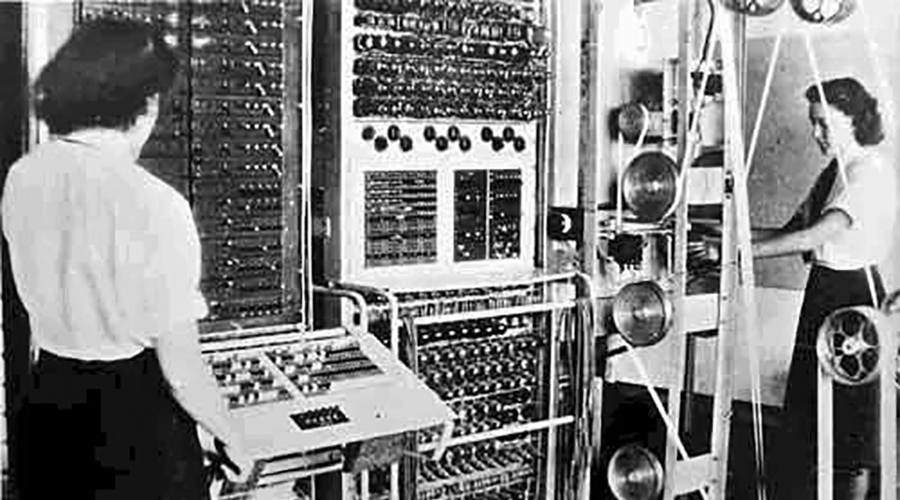
Colossus was the world's first electronic digital computer that was programmable. The Colossus computers were developed for British codebreakers during World War II to help in the cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher. Without them, the Allies would have been deprived of the very valuable military intelligence that was obtained from reading the vast quantity of encrypted high-level telegraphic messages between the German High Command (OKW) and their army commands throughout occupied Europe. Colossus used thermionic valves (vacuum tubes) to perform Boolean operations and calculations.
Colossus was designed by the engineer Tommy Flowers to solve a problem posed by mathematician Max Newman at the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park. Alan Turing's use of probability in cryptanalysis contributed to its design. It has sometimes been erroneously stated that Turing designed Colossus to aid the Cryptanalysis of the Enigma Turing's machine that helped decode Enigma was the electromechanical Bombe, not Colossus.