Go backward to APPENDIX A: MATHEMATICAL BACKGROUND
Go up to Top
Go forward to References
APPENDIX B: NOTES
Definitions of the Fourier transform vary in the literature:
there is a choice of constant factors in front
of the integral and/or in the exponent inside the integral.
In particular, i may be replaced by -i.
For instance, if we define the Fourier transform to be
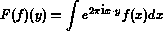
and its inverse transform to be
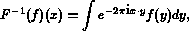
then the Fourier inversion formula says that
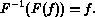
Chee Yap