 MISHRA 95
MISHRA 95
Lecture #5
Programming Languages  MISHRA 95
MISHRA 95
---Slide 2---
The Design History
---Slide 3---
Quick Overview
---Slide 4---
Ada Type System
attributes
type <identifier> is <type-definition>
<variable> : <type>
<name>'<attribute-identifier>
---Slide 5---
Examples
type DAY is (MON,TUE,WED,THU,FRI,SAT,SUN);
--Enumeration Type
TODAY: DAY; TOMORROW: DAY; CURRENT_DAY: DAY;
HOURS_WORKED: array(DAY'FIRST..DAY'LAST)
of INTEGER;
if TODAY <= FRI then
TOMORROW := DAY'SUCC(TODAY);
for CURRENT_DAY in DAY'FIRST..DAY'LAST loop
...
end loop;
---Slide 6---
Primitive Scalar Types
INTEGER =
SYSTEM.MIN_INT..SYSTEM.MAX_INT
+, -, *, / (Arithmetic operations)<, <=, =, /=, >=, >
(Logical operations)
---Slide 7---
Discrete Types
Characters = 128 ASCII characters: 'A', 'B',
'C', 
Booleans = FALSE & TRUE
FALSE <
TRUE.
T )
T'POS:
SUIT'POS(HEARTS) = 0
T'VAL:
POS
SUIT'VAL(0) = HEARTS
T'SUCC, T'PRED
T'FIRST, T'LAST
---Slide 8---
Real Type
type WEIGHT is digits 10;Values have an accuracy of 10 digits.
type VOLTAGE is delta 0.1 range 0.0..1.0;Values have an accuracy at least as fine as 0.1.
FX = Fixed Point: 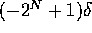 ..
..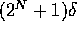
FX'DELTA, FX'LARGE
FL = Floating Point:
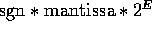 ; mantissa has B digits.
; mantissa has B digits.
FL'DIGITS, FL'MANTISSA, FL'EMAX, FL'SMALL, FL'LARGE, FL'EPSILON
---Slide 9---
Derived Type
subtype BYTE_SIZE is INTEGER range -2**7..2**7; subtype CAPS is CHARACTER range 'A'..'Z'; subtype <identifier> is <parent-type> range <constraint>;
X, Y: constant INTEGER range 0..128 = abs(N);
<identifier>: <mutability> <type> <constraint>
= <init-value>;
if CURRENT_INPUT not in CAPS then ...
---Slide 10---
Assignment Statement
X := Y;
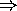
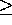 type(Y)
type(Y)
constraint exception.
---Slide 11---
Examples
subtype NATURAL is INTEGER range 1..INTEGER'LAST; A: INTEGER; B: FLOAT; C: NATURAL; D: INTEGER range 0..INTEGER'LAST; A := B; --illegal A := INTEGER(B); --type conversion, legal A := C; --legal A := D - 3; --legal A := C + INTEGER(B); --legal C := D; --constraint exception C := A; --constraint exception
---Slide 12---
Arrays

subtype NATURAL is INTEGER range 1..INTEGER'LAST;
type SHORT_STRING is array(1..10) of CHARACTER;
type STRING is
array (NATURAL range <>) of CHARACTER;
NAME: STRING(1..10);
---Slide 13---
Array Assignment
B to A: A := B
A is same as type of B.
A has same number of elements as B, then
B is copied into A positionally---Otherwise,
constraint-error exception is raised.
declare A: STRING(1..10); B: STRING(11..20); begin A := B; end;
---Slide 14---
Array Indexing & Slicing
S: STRING(1..10); S(3) := S(2);
S(3..7) --an array object S(3..7) := S(4..8); S := S(2..10) & S(1) -- & == concatenation opn
type SYM_TAB is array (CHARACTER range <>) of INTEGER;
TABLE: SYM_TAB('a'..'c') := (0, 1, 2);
TABLE := ('c' => 2, 'b' => 1, 'a' => 0);
TABLE := ('c' | 'b' => 1, others => 0);
---Slide 15---
Records
MY_CAR.CAR_MAKE
type CAR_MAKE is (FORD, GM, HONDA); subtype CAR_YEAR is INTEGER range 1900..1999; type CAR is MAKE: CAR_MAKE; YEAR: CAR_YEAR; end record; MY_CAR: CAR;
---Slide 16---
Records (Contd)
B may be assigned to record A, provided
they have same type.
A, B: CAR; A := B;
YOUR_CAR: CAR := YOUR_CAR: CAR :=
(GM, 1981); (MAKE => GM,
YEAR => 1981);
---Slide 17---
Variant Records
type VEHICLE_TAG is (CAR, TRUCK);
type VEHICLE(TAG: VEHICLE_TAG) is record
YEAR: MODEL_YEAR := 93;
case TAG is
when CAR => COLORS: COLOR_SCHEME;
when TRUCK => AXLES: NATURAL;
end case;
end record;
YOUR_TRUCK: VEHICLE(TRUCK);
REFRIGERATOR: VEHICLE; --Illegal
type BUFFER(LENGTH: NATURAL) is record
POOL: STRING(1..LENGTH);
end record;
---Slide 18---
Access Types
type STRING_PTR is access STRING;
type STRING_10_PTR is access STRING(1..10);
P, Q: STRING_PTR; P10: STRING_10_PTR;
P10 := new STRING(1..10);
P10 := new STRING(2..11); --Constraint Error
P10 := new STRING; --Illegal
P := new STRING(1..3); --OK
P.all := "BUD";
Q := new STRING("MUD");
P := Q;
P.all := Q.all
new creates a new object that can be designated by the
access type.
---Slide 19---
Recursive Types
type NODE; --Incomplete Declaration;
type NODE_PTR is access NODE;
type NODE is
record
DATUM: CHARACTER;
NEXT: NODE_PTR;
end record;
---Slide 20---
Control Structures
DISCRIM := (B**2 - 4.0*A*C);
TABLE(J) := TABLE(J) + 1;
VECTOR := (1..10 => 0);
if (A=1) then
...
end if; case A is
when 1 => --...;
if (A=1) then when 2 => --...;
--... when others => null;
elsif (A=2) then end case;
--...
else
--...
end if;
---Slide 21---
Control Structures: Iteration Clause
loop
-- Statements to be repeated
end loop;
loop terminates when
SUM := 0; SUM := 0;
for I in 1..10 loop for I in reverse 1..10 loop
SUM := SUM + A(I); SUM := SUM + A(I);
end loop; end loop;
SUM := 0; I := 1; SUM := 0; I := 1;
while I <= 10 loop loop
SUM := SUM + A(I); exit when I > 10;
I := I + 1; SUM := SUM + A(I);
end loop; I := I + 1;
end loop;
---Last Slide---
A Complete Ada Program
with I_O_PACKAGE;
procedure TEMPERATURE_CONVERSION is
use I_O_PACKAGE;
-- Convert temp in Fahrenheit to Celsius
FAHRENHEIT_TEMP; CELSIUS_TEMP: FLOAT;
begin
GET(FAHRENHEIT_TEMP);
CELSIUS_TEMP := (FAHRENHEIT_TEMP - 32.0)*5.0/9.0;
PUT(CELSIUS_TEMP);
end TEMPERATURE_CONVERSION;
[End of Lecture #5]