================ Start Lecture #20
================
4.4.5: Design principles for security
More bathroom reading
4.4.6: User authentication
Passwords
- Publically available cracking software
- Use this software for prevention
- One time passwords: e.g. SecurId.
- Current practice here and elsewhere is that when you telnet to a
remote machine, your password is sent in the clear along the ethernet.
So maybe .rhosts is aren't that bad after all.
- Physical identification: Opens up a bunch of privacy questions.
Should we require fingerprinting for entering the subway?
Homework: 15, 16, 19, 24.
4.5: Protection mechanisms
4.5.1: Protection domains
- Objects (passive) and subjects (active)
For example processes examine files
- Protection domain: A collection of (object,
rights) pairs
- At any given time a subject is given a protection domain that
specifies its rights.
- In Unix a subject's domain is determined by its (uid, gid) (and
whether it is in kernel mode).
- Generates a matrix called the protection or permission matrix
- Each row corresponds to a domain (i.e. a subject at some time)
- Each column corresponds to an object (e.g. file, device)
- Each entry gives the rights the domain/subject has on this object
- Can model Unix suid/sgid by permitting columns whose headings are
domains and the only right possible in the corresponding entries is
entry. If this right is there the subject can s[ug]id to this new domain.
4.5.2: Access Control Lists (ACLs)
Keep the columns of the matrix separate and only keep the non-null
entries.
4.5.3: Capabilities
Keep the rows of the matrix separate and only keep the non-null
entries.
4.5.4: Protection models
Give objects and subjects security levels and enforce
- A subject may read only those objects whose level is at or below
her own.
- A subject may write only those objects whose level is at or
above her own.
4.5.5: Covert channels
The bad guys are getting smart and use other means of getting out
information. For example give good service for a zero and bad for a
one. The figure of merit is what rate can bits be sent, i.e. the
bandwidth of the covert channel.
Homework: 20.
Chapter 5: Input/Output
5.1: Principles of I/O Hardware
5.1.1: I/O Devices
- Not much to say. Devices are varied
- Block versus character devices:
- Devices, like disks or CDROMs, with addressable chunks
(sectors in this case) are called block
devices.
These devices do not support seeking.
- Devices, like an Ethernet or modem connection, that are a
stream of characters are called character
devices
These devices do not support seeking
- Some cases, like tapes, are not so clear
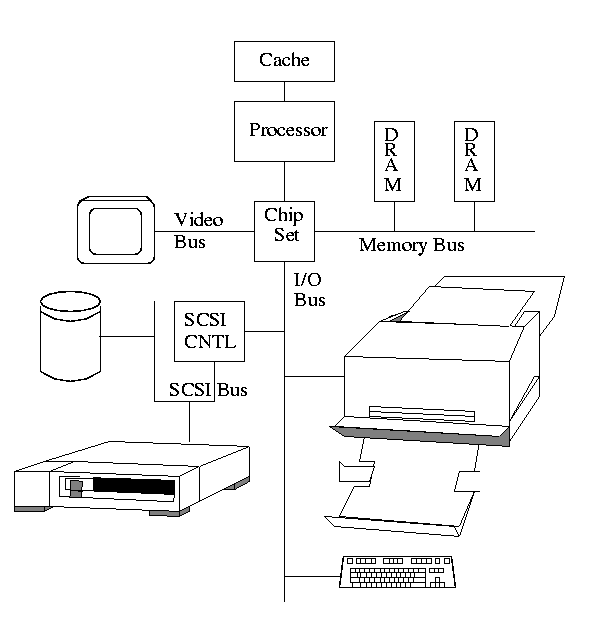
5.1.2: Device Controllers
These are the ``real devices'' as far as the OS is concerned. That
is the OS code is written with the controller spec in hand not with
the device spec.
The figure in the book is so oversimplified as to be borderline
false. The following picture is closer to the truth (but really there
are several I/O buses of different speeds).