================ Start Lecture #8
================
Chapter 3: Memory Management
Also called storage management or
space management.
Memory management must deal with the storage
hierarchy present in modern machines.
- Registers, cache, central memory, disk, tape (backup)
- Move date from level to level of the hierarchy.
- How should we decide when to move data up to a higher level?
- Fetch on demand (e.g. demand paging, which is dominant now)
- Prefetch
- Read-ahead for file I/O
- Large cache lines and pages
- Extreme example. Entire job present whenever running.
We will see in the next few lectures that there are three independent
decision:
- Segmentation (or no segmentation)
- Paging (or no paging)
- Fetch on demand (or no fetching on demand)
Memory management implements address translation.
- Convert virtual addresses to physical addresses
- Also called logical to real address translation
- Virtual address is the address expressed in the program
- Physical address is the address understood by the computer
- The translation from virtual to physical addresses is performed by
the Memory Management Unit or (MMU).
- Another example of address translation is the conversion of
relative addresses to absolute addresses by the linker.
- The translation might be trivial (e.g., the identity) but not in a modern
general purpose OS.
- The translation might be difficult (i.e., slow)
- Often includes addition/shifts/mask--not too bad
- Often includes memory references
- VERY serious
- Solution is to cache translations in a Translation
Lookaside Buffer (TLB). Sometimes called a
translation buffer (TB)
Homework: 7.
When is the address translation performed?
- At compile time
- Primitive
- Compiler generates physical addresses
- Requires knowledge of where the compilation unit will be loaded
- Rarely used (MSDOS .COM files)
- At link-edit time (the ``linker lab'')
- Compiler
- Generates relocatable addresses for each compilation unit
- References external addresses
- Linkage editor
- Converts the relocatable addr to absolute
- Resolves external references
- Misnamed ld by unix
- Also converts virtual to physical addresses by knowing where the
linked program will be loaded. Unix ld does
not do this.
- Loader is simple
- Hardware requirements are small
- A program can be loaded only where specified and
cannot move once loaded.
- Not used much any more.
- At load time
- Same as linkage editor but do not fix the
starting address
- Program can be loaded anywhere
- Program can move but cannot be split
- Need modest hardware: base/limit registers
- At execution time
- Dynamically during execution
- Hardware needed to perform the virtual to physical address
translation quickly
- Currently dominates
- Much more information later
Extensions
- Dynamic Loading
- When executing a call, check if module is loaded.
- If not loaded, call linking loader to load it and update
tables.
- Slows down calls (indirection) unless you rewrite code dynamically
- Dynamic Linking
- The traditional linking described above is now called
statically linked
- With dynamic linking frequently used routines are not linked
into the program. Instead, just a stub is linked.
- When the routine is called, the stub checks to see if the
real routine is loaded (it may have been loaded by
another program).
- If not loaded, load it.
- If already loaded, share it. This needs some OS
help so that different jobs sharing the library don't
overwrite each other's private memory.
- Advantages of dynamic linking
- Saves space: Routine only in memory once even when used
many times
- Bug fix to dynamically linked library fixes all applications
that use that library, without having to
relink the application.
- Disadvantages of dynamic linking
- New bugs in dynamically linked library infect all
applications
- Applications ``change'' even when they haven't changed.
Note: I will place ** before each memory management
scheme.
3.1: Memory management without swapping or paging
Job remains in memory from start to finish
The sum of the memory requirements of all jobs in the system cannot
exceed the size of physical memory.
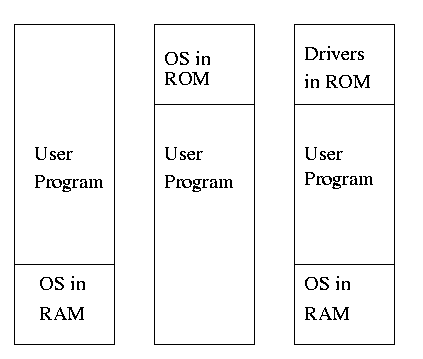
** 3.1.1: Monoprogramming without swapping or paging (Single User)
The ``good old days'' when everything was easy.
- No address translation done by OS (i.e., address translation is
not performed dynamically during execution).
- Either reload OS each job (or don't have an OS, which is almost
the same) or protect the OS from the job.
- One way to protect (part of) the OS is to have it in ROM.
- Of course, must have the data in ram
- Can have a separate OS address space only accessible in
supervisor mode.
- User overlays if job memory exceeds physical memory.
- Programmer breaks program into pieces.
- A ``root'' piece is always memory resident.
- The root contains calls to load and unload various pieces.
- Programmer's responsibility to ensure that a piece is already
loaded when it is called.
- No longer used, but we couldn't have gotten to the moon in the
60s without it (I think).
- Overlays have been replaced by dynamic address translation and
other features (e.g., demand paging) that have the system support
logical address sizes greater than physical address sizes.
- Fred Brooks (leader of IBM's OS/360 project, author of ``The
mythical man month'') remarked that the OS/360 linkage editor was
terrific, especially in its support for overlays, but by the time
it came out, overlays were no longer used.
3.1.2: Multiprogramming
Goal is to improve CPU utilization, by overlapping CPU and I/O
- Consider a job that is unable to compute (i.e., it is waiting for
I/O) a fraction p of the time.
- Then for monoprogramming the CPU utilization is 1-p.
- Note that p is often > .5 so CPU utilization is poor.
- But with a multiprogramming level (MPL) of n, the
CPU utilization is approximately 1-p^n.
- If p=.5 and n=4, then 1-p^n = 15/16, which is much better.
- The rationale for the above formula is that, if the probability that a
job is waiting for I/O is p and n jobs are in memory, then the
probability that all n are waiting for I/O is p^n.
- This is a crude model, but it is correct that increasing MPL does
increase CPU CPU utilization.
- The limitation is memory, which is why we discuss it here
instead of process management. That is, we must have many jobs
loaded at once, which means they can't all be loaded at the same
place. There are other issues as well and we will discuss them.
- Some of the CPU utilization is time spent in the OS executing
context switches.

